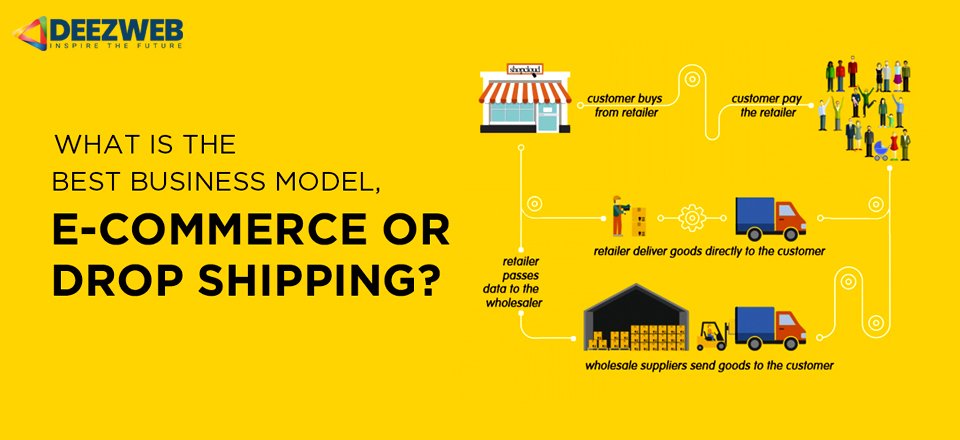
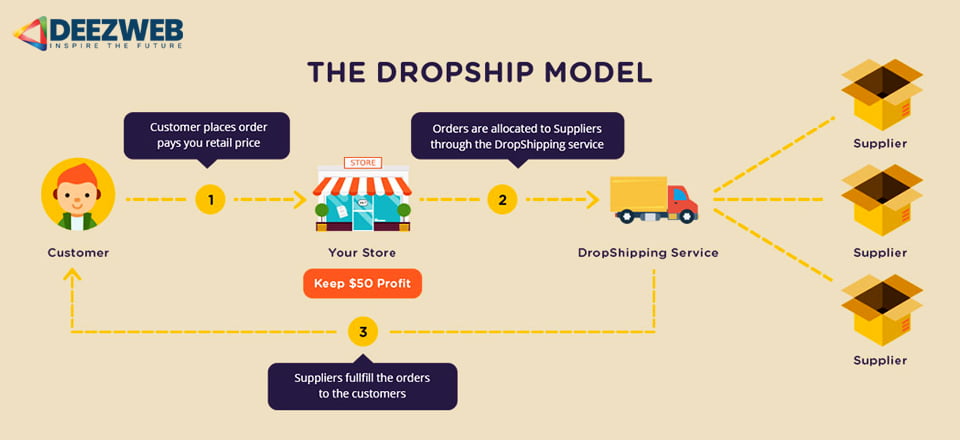
Many of us dream of starting our own business. When looking around, it’s tempting to think, “Hey, anyone can do this!” But it’s important to remember that there’s a difference between merely starting a business on paper and setting yourself up for success. Done correctly, it takes careful planning, investment, and motivation. Going in blind and starting a business without knowing what you’re getting into can lead to costly failure.
In this article, we’ll attempt to take as much of the guesswork out of the process as possible by showing you how to start a business in 13 general steps. Some of these steps will be slightly different based on the region you live in. For example, the “legal stuff” in this article specifically focuses on the US.
That said, no matter where you reside we recommend checking with a local lawyer and your local government to determine any legal requirements for starting a business in your area. Nothing in this article should be considered legal advice.
With that caveat out of the way, let’s talk about what you need to do to not only start your business but set yourself up for success!
1. Start with You
Don’t just jump in. Make sure you have what it takes to run your own business. Don’t limit yourself, but evaluate yourself to know who you’re dealing with. Know your strengths, weaknesses, likes, dislikes, tastes, and interests. Know your skills, passions, the lifestyle you’re after, how much you can spend, how much you can afford to risk, and the types of work you want to do.
Not everyone can be their own boss. It takes motivation and discipline to see the project through and it’s difficult to stick with something you don’t like. It’s okay if you don’t know much about business itself at first. Take courses if you need to. The important thing is that you’re completely invested in (and a good fit for) the work required for the business you choose to create.
2. The Business Idea
It pays to spend some time on the business idea. Here are a few things to ponder:
Maybe you have a better solution to an annoying problem. What problems can you solve?
Look at what’s coming soon in various industries such as technology, health, entertainment, etc. Ask how it will change life or business in general and what you can do to position yourself (and your business) to capitalize on that change.
How can you apply your skills to a different industry? For example, do you have a unique skill set or way of thinking learned in one industry that has yet to be applied to another? Perhaps there’s opportunity there?
Can you provide something better or cheaper than it’s currently being provided? Can you provide something to a location that doesn’t have access to it?
You can also search the web for business ideas and take note of those that sound like a good fit for you.
One method is to ask yourself a few simple questions that will help you narrow down your options:
- What are your strengths?
- Of those strengths, what is in demand?
- Of what is in demand, what can you afford to provide?
Once you have a few ideas, run them by someone you trust that has a strong sense of business. Ask for advice from other entrepreneurs that you trust.
3. Perform Market Research
Once you have your business idea, research it to make sure that it’s in demand, that there’s room in the market for you, and that you can afford to provide it. Perform a SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats).
Research your competitors and the market demand in the area you’ll provide the business. This might require you to interview businesses to see if they need your product or service.
You have to figure out your unique advantage–often referred to as a unique selling proposition. Your business will fail if you’re number 75 trillion on Google that’s offering the same service. How are you different? What can you do that they’re not doing?
It’s important to do your own research. Someone else’s research might not be complete or it could be out of date. They may have focused on a different point than you need to. Also, don’t just search online. Go to the source. The more time you invest up front the fewer problems you’ll run into later.
4. Write a Business Plan
A business plan is a written description of your business. It works like a roadmap and should be updated over time. It helps give you the information you need to develop the business and get funding (or what it will take to bootstrap, if that’s the path you choose). It also provides projections to help you decide how viable your idea is.
There are several ways to create a business plan. The Small Business Administration recommends creating a detailed description of each point in this structure”
- Executive summary – a high-level summary
- Company description – describes the business
- Market analysis – target market, competitors, etc.
- Organization and management – who does what and why they’re qualified
- Service or product line – details about the products
- Marketing and sales – what are the sales channels and what is the strategy
- Funding request – what is needed, how it will be used, when it will be paid back
- Financial projections – how much the company will make and when for 5 years
- Appendix – projections, resumes, licenses, contracts, etc.
Generally speaking, it should have 20-30 pages and a 10-page appendix. This is the traditional route and more companies are familiar with it, so this is what we recommend if you’re planning to get funding. The business plan provides the information you’ll need for the rest of this list.
Remember: it should be revised as time goes on. Don’t be afraid of making changes. Every good business makes course corrections.
5. Plan Your Funding
Determine how much funding you’ll need, when you’ll need it by, and when the company will start making a profit. Use this information to pitch potential investors and secure the funding you need.
You have several options:
- Self-funding (Bootstrapping)
- Friends and family
- Grants
- Angel investors
- Venture capitalists
- Crowdfunding
- Advance from customers
- Trade equity
- Loan from partners
- Bank loan
- Business credit line
Out of these options the easiest sources of funding to secure are self-funding (of course) and a business credit line. Depending on the business you’d like to start however, these options may not provide enough money all at once for you to do what you need to do. That’s where actual outside investment becomes necessary.
6. Choosing the Business Structure
Before making your business official you’ll need to decide what type of entity it is. This will determine how you file taxes, liability, etc. The main entities include:
- Sole Proprietorship – you are the only owner and you’re responsible for all debts and it can directly affect your personal credit.
- Partnership – you have one or more partners and you’re all responsible for all debts.
- Corporation – the business is its own entity and it is responsible for its own liabilities.
- Limited Liability Corporation (LLC) – the business has the legal protections of a corporation and the tax benefits of a partnership.
7. Choose and Register Your Business Name
Find a name that matches your brand and mission. Choose something that makes sense for your niche or industry. Make sure it isn’t already in use, and make sure to get the domain name and social user names.
8. Open a Business Bank Account
Open a checking account specifically for the business in order to keep it separated from your personal accounts. This will help with daily spending, bills, legal, and taxes, and will look more professional so others will take it seriously.
9. Get Your Tax IDs, Licenses, and Permits
Be sure to get all of the required licenses and permits. This includes state and local registration. The exact licenses and permits will be different depending on the type of business and product or service you’re providing.
10. Your Business Location
Set up your office and anything else your business requires to operate. This includes all of the equipment, furniture, supplies, etc. Make sure to choose a location that works for your business. There may be restrictions for certain locations.
For example, some equipment may not be allowed in residential areas, or you may have zoning issues for the types of businesses that are allowed. Even if it’s a home office, be sure to include the cost in your business expenses.
11. Build Your Team
If you’re hiring team members, be sure to follow local legal guidelines. Set clear goals and responsibilities, develop great communication channels, and set a strong company culture. Make sure everyone is a good fit for the company’s goals and vision.
Even if your business is a sole proprietorship, it’s a good idea to have a team mindset. You might need to partner with others to perform tasks that you don’t want to do or don’t have time to do. For example, you might want to hire someone to write for your blog, handle social media, create the graphics for your website, etc.
12. Create the Product or Service
You’ll need actual examples of the products or services. This can be as simple as a portfolio to show examples of the work, the first phase of software, the first run of a manufactured product, etc. It needs to be something viable and not just a mockup. It doesn’t have to have all the bells and whistles at launch. Those can be added later. Remember, Divi was started as 1.0., not 3.0.
13. Promote Your Business
No matter how amazing your product or service is, it won’t help anyone if no one knows about it. You must promote your business to your target market. An essential element in promoting your business is having an amazing website and a strong social media presence. Develop your website to bring in organic traffic. Run ad campaigns when and where appropriate. Build your email list.
Once you’ve started making sales, ask for feedback and listen to your customers and make changes as needed. Build a strong relationship with your customers. Continuously add value and improve the quality of your products or services.
Ending Thoughts
Some of these steps can be done in a different order, but you do need all of these in order to start a business. There aren’t a lot of shortcuts when it comes to establishing a successful business. It takes time, planning, investment, and effort. Once you get your business started you’ll need to keep improving, keep competing, keep investing, and keep marketing. Make smart changes as needed and don’t give up.
We want to hear from you. Have you followed, or plan to follow, these steps in building your own business? Let us know about it in the comments.